Elasticsearch基础查询详解

批量插入数据
使用以下语句在myindex索引库中批量插入数据:
POST myindex/_bulk
{"index": {}}
{"name": "张三", "address": "中国", "age": 18}
{"index": {}}
{"name": "李四", "address": "中国", "age": 19}
{"index": {}}
{"name": "王五", "address": "美国", "age": 20}
{"index": {}}
{"name": "赵六", "address": "美国", "age": 28}查询所有数据
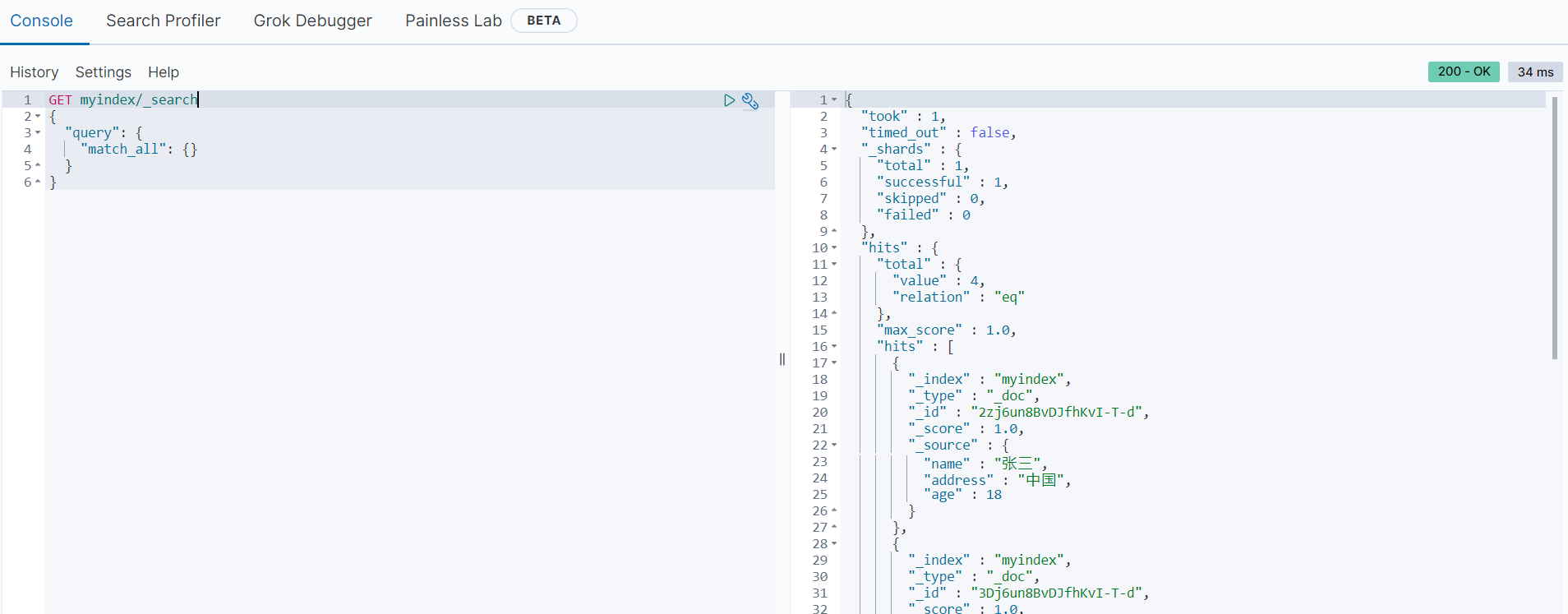
使用以下语句可以查询当前索引库中所有的文档数据:
GET myindex/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}返回结果如下:
以下字段为返回信息中的重要信息:
排序查询
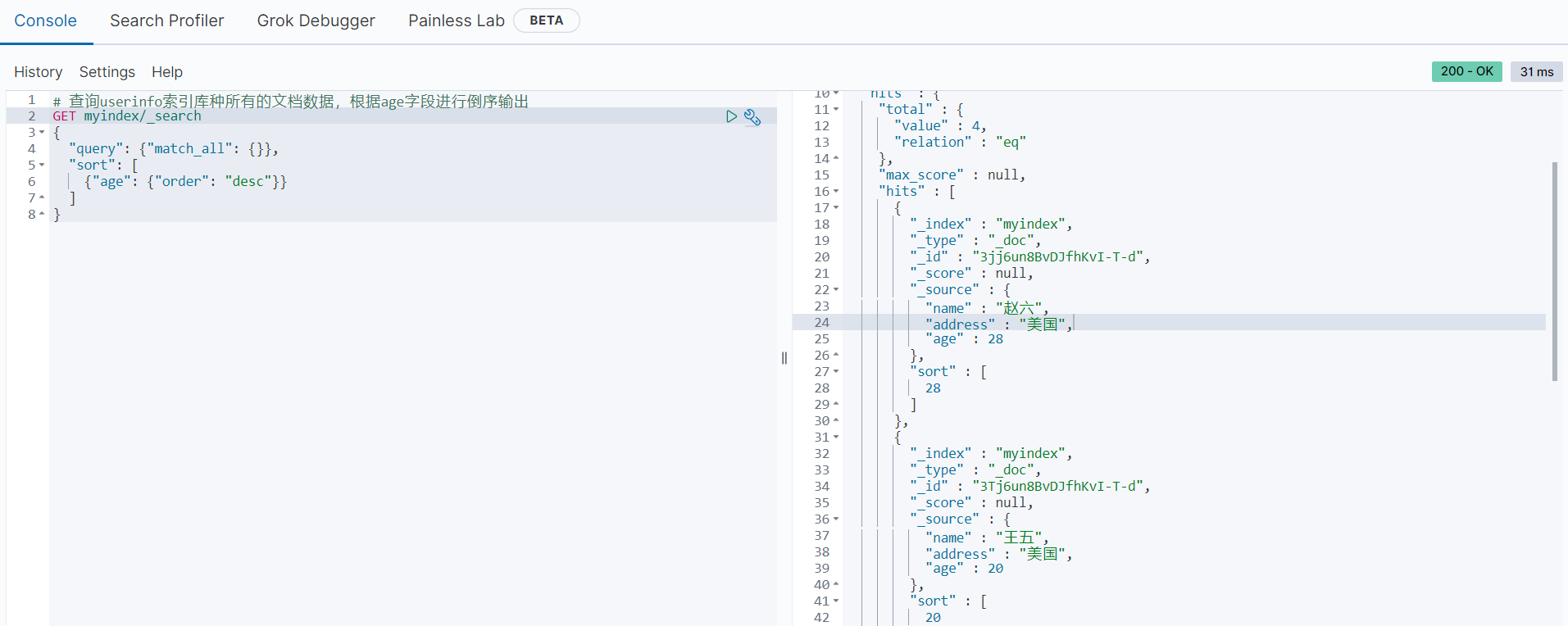
下面是进行排序查询的范例:
# 查询userinfo索引库种所有的文档数据,根据age字段进行倒序输出
GET myindex/_search
{
"query": {"match_all": {}},
"sort": [
{"age": {"order": "desc"}}
]
}执行结果如下图所示:
如果需要按顺序排序,则可以使用下面的语句:
GET myindex/_search
{
"query": {"match_all": {}},
"sort": [
{"age": {"order": "asc"}}
]
}如果需要根据多个字段排序,则可以使用下面的语句:
GET /索引名称/_search
{
"query": {"match_all": {}},
"sort": [
{"field1": {"order": "desc"}},
{"field2": {"order": "asc"}}
]
}以上语句表示先根据field1字段进行倒序排序,再根据field2字段进行顺序排序。需要注意的是,排序字段不可以是text等特殊类型,一般是整数类型和keyword类型。
根据需求返回相应的字段
在生产环境中,对数据库的操作时可能不需要返回所有的字段内容,只返回所需的部分字段的内容。使用Elasticsearch返回指定段数据的语法如下:
GET 索引名称/_search
{
"query": {查询语句},
"_source": ["字段1", "字段2", "字段3", ...]
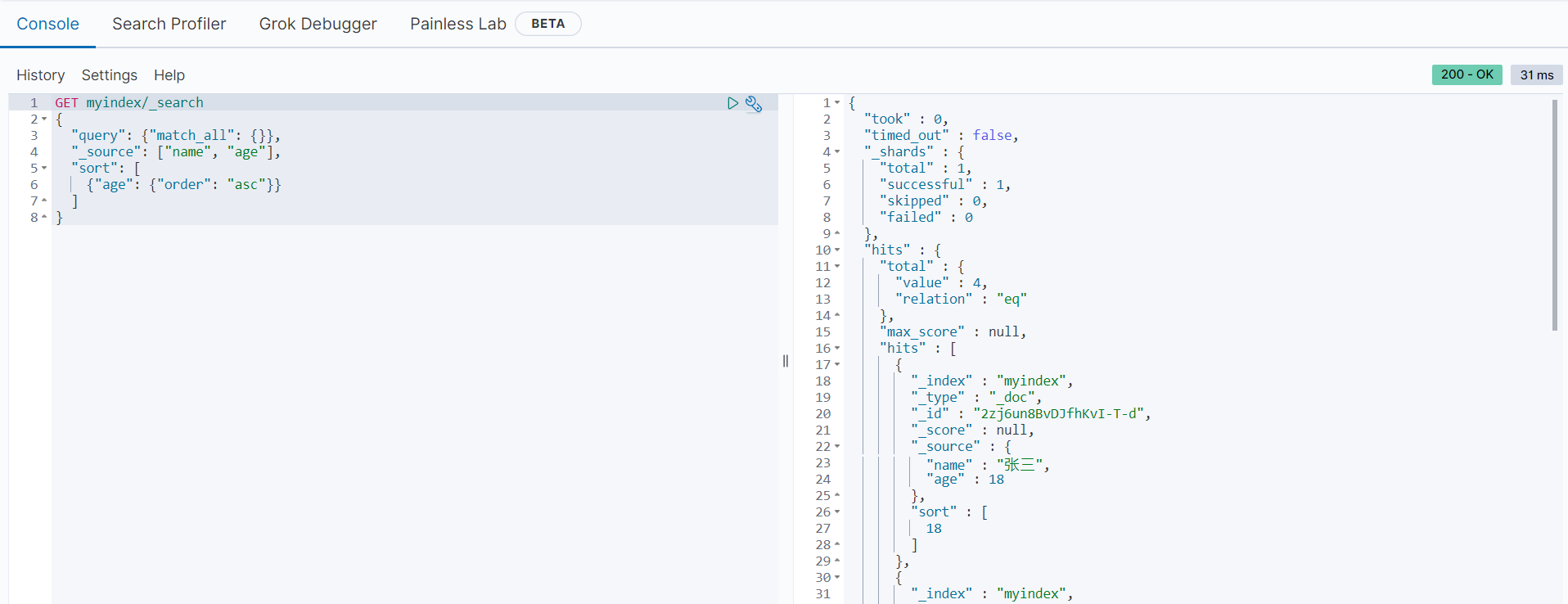
}范例如下:
GET myindex/_search
{
"query": {"match_all": {}},
"_source": ["name", "age"],
"sort": [
{"age": {"order": "asc"}}
]
}返回结果如下:
由上可知,在返回的所有数据中,从每一个文档只返回了name和age字段的内容,而且输出顺序符合预期,根据年龄大小的顺序排序输出。
分页查询
Elasticsearch可以利用from和size两个字段进行分页查询,语法如下:
GET 索引名称/_search
{
"query": {查询语句},
"_source": ["字段1", "字段2", ...],
"from": 0,
"size": 10
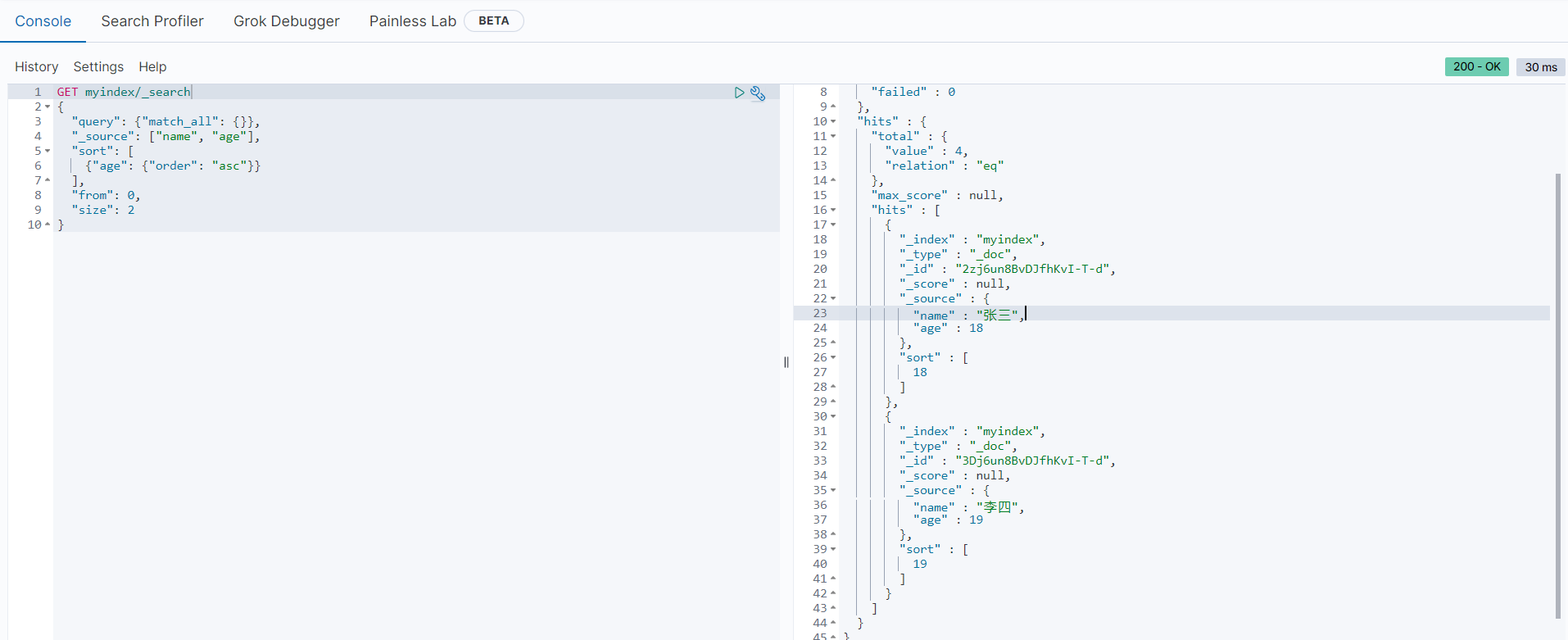
}范例如下:
GET myindex/_search
{
"query": {"match_all": {}},
"_source": ["name", "age"],
"sort": [
{"age": {"order": "asc"}}
],
"from": 0,
"size": 2
}以上语句将查询索引库种的所有文档数据,并根据age字段按顺序排序,返回从第0条到第2条的文档数据,只包含name和age字段的内容,执行结果如下所示:
可以看到,符合条件的数据文档数量是4条(hits.total.values = 4),因为我们的分页语句要求返回两条数据,所以hits对象中只包含”张三“和”李四“两条数据,并且根据age字段按顺序输出,返回结果符合预期。
查询指定字段内的特定字词
如果想要在Elasticsearch种查询指定字段内的特定字词,可以使用match进行查询,其语法如下:
GET 索引名称/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"field": "查询内容"
}
}
}范例如下:
GET myindex/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address": "中国"
}
}
}段落匹配查询
为了更好地理解段落匹配,我们先了解一下下面这个范例:
# 批量插入数据
POST myindex/_bulk
{"index": {}}
{"name": "张三", "address": "中国 上海", "age": 18}
{"index": {}}
{"name": "李四", "address": "中国 上海", "age": 19}
{"index": {}}
{"name": "王五", "address": "中国 杭州", "age": 20}
{"index": {}}
{"name": "赵六", "address": "中国 杭州", "age": 21}
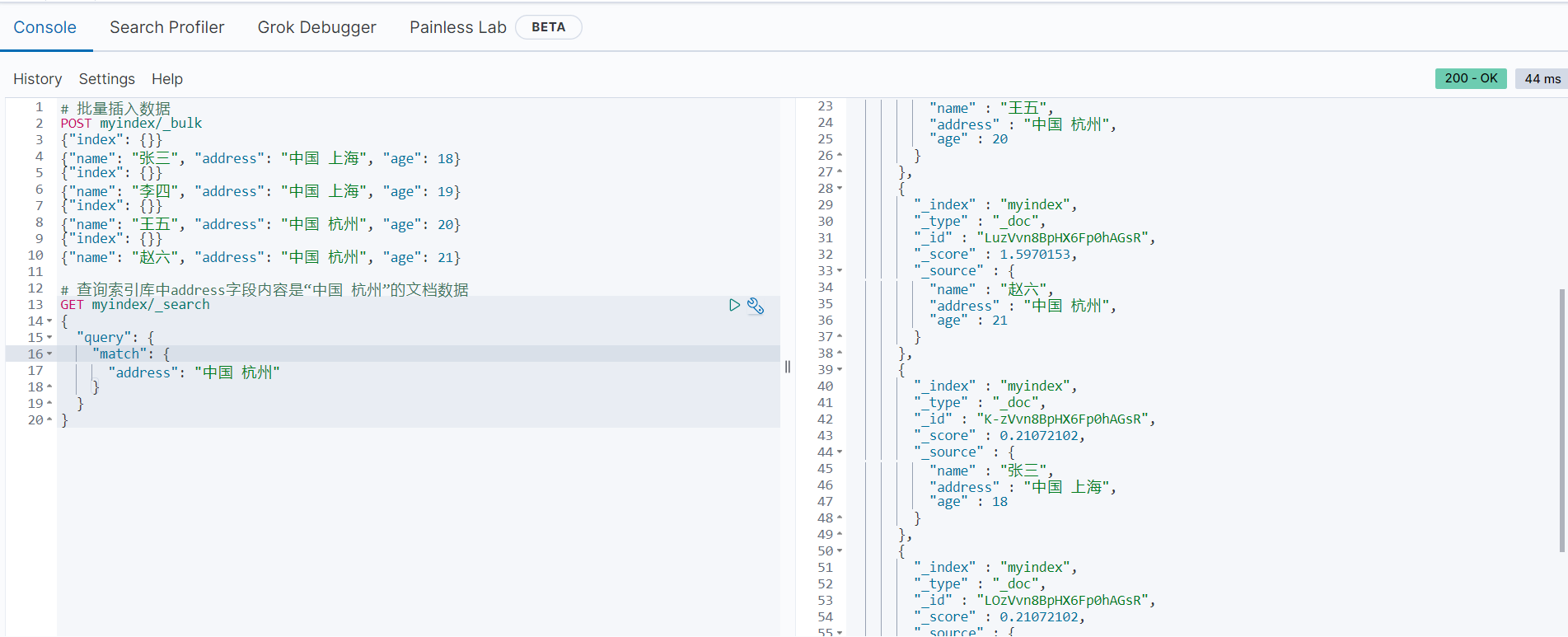
# 查询索引库中address字段内容是“中国 杭州”的文档数据
GET myindex/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address": "中国 杭州"
}
}
}查询结果如下:
由以上结果可知,因为查询的时候两个内容之间由空格,所以被当作分隔符处理,查询内容被分词,如果想要查询的内容不被分词,可使用match_phrase查询,语法如下:
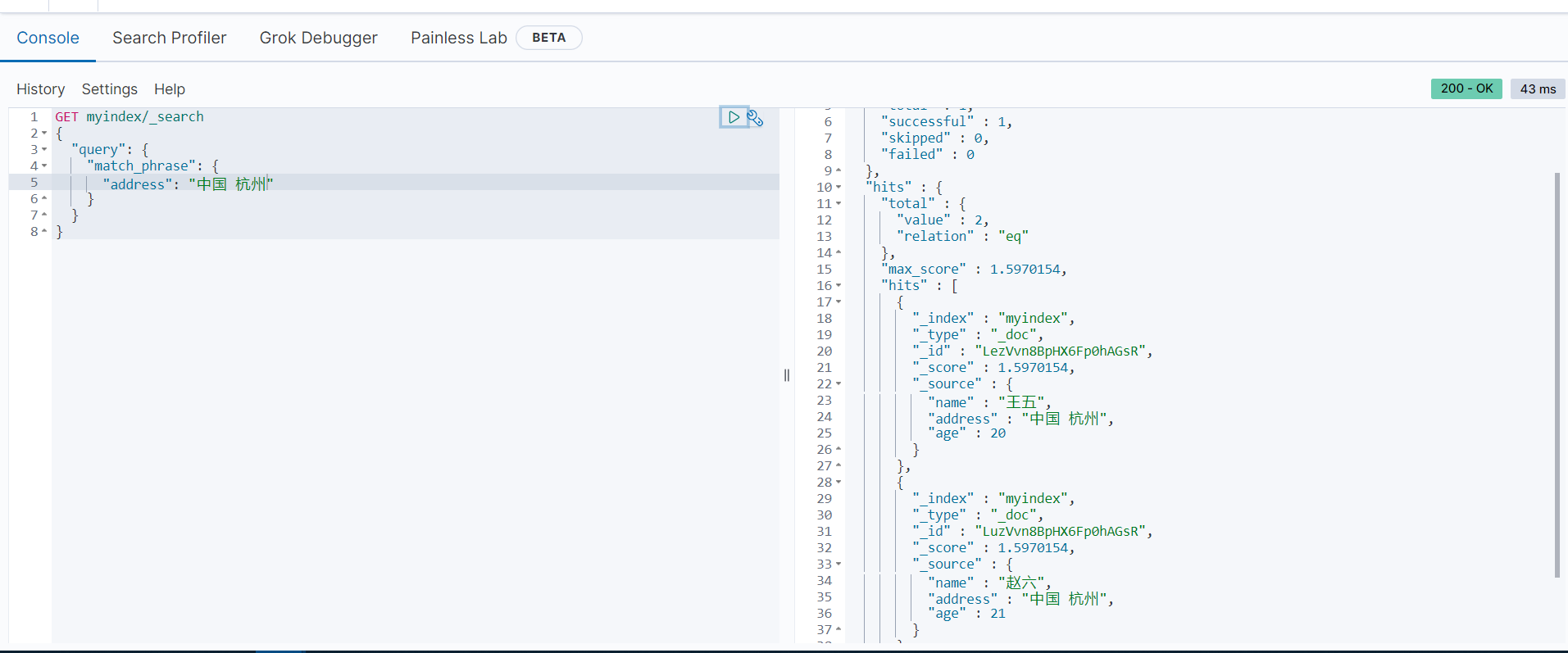
GET myindex/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"address": "中国 杭州"
}
}
}可以看到,结果中只返回了“王五”和“赵六”的文档信息,而其对应的address字段的值都是“中国 杭州”,返回的结果符合预期。
term精准查询
在Elasticsearch中使用term和前面使用match_phrase的效果类似。如下范例是创建一个索引模板,其address字段在存储的时候使用ik_max_word模式进行分词存储,而查询的时候根据standard分词器的默认模式(中文语句会被拆成一个个汉字)进行查询。
PUT myindex
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"address": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer": "standard"
},
"age": {
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
}
POST myindex/_bulk
{"index": {}}
{"name": "张三", "address": "魏国", "age": 18}
{"index": {}}
{"name": "李四", "address": "蜀国", "age": 19}
{"index": {}}
{"name": "王五", "address": "吴国", "age": 20}
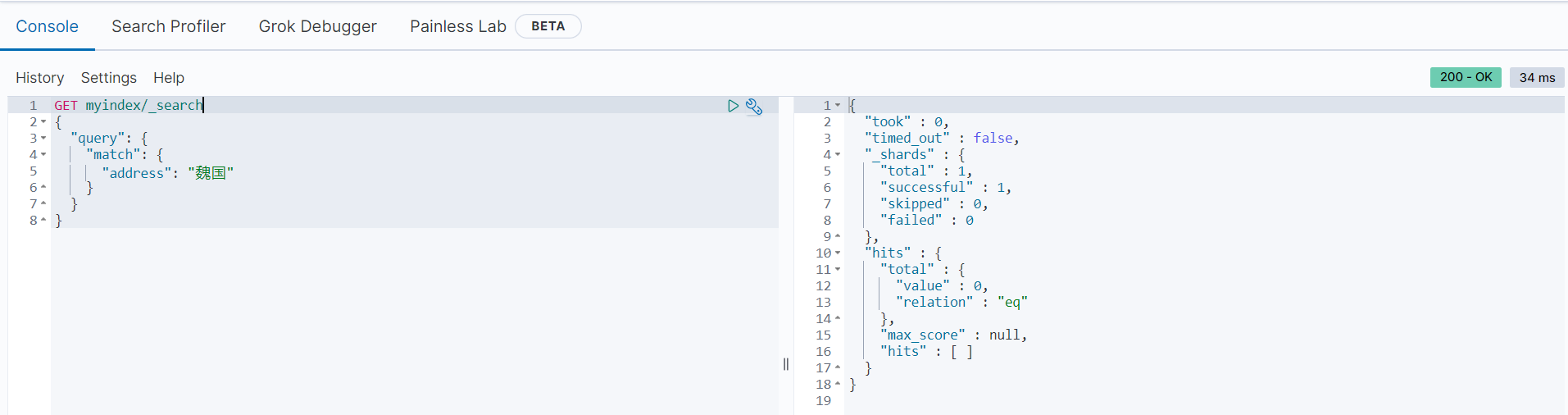
GET myindex/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address": "魏国"
}
}
}执行结果如下:
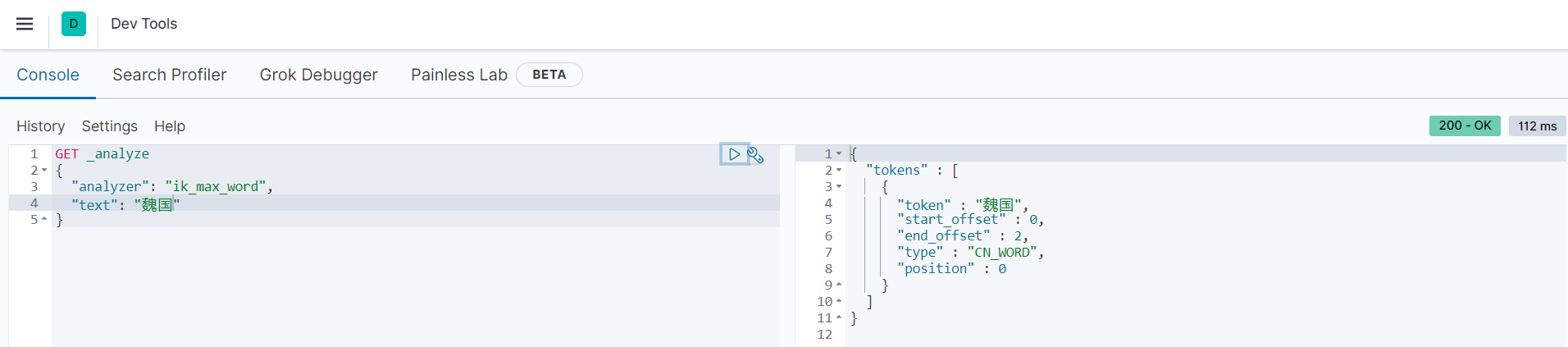
可以看到,返回结果中没有匹配的文档数据,这是因为在存储的时候,”魏国“、”蜀国“、”吴国“经过ik_max_word模式进行分词,分词之后的内容依旧是”魏国“、”蜀国“、”吴国“。分词结果如下所示:
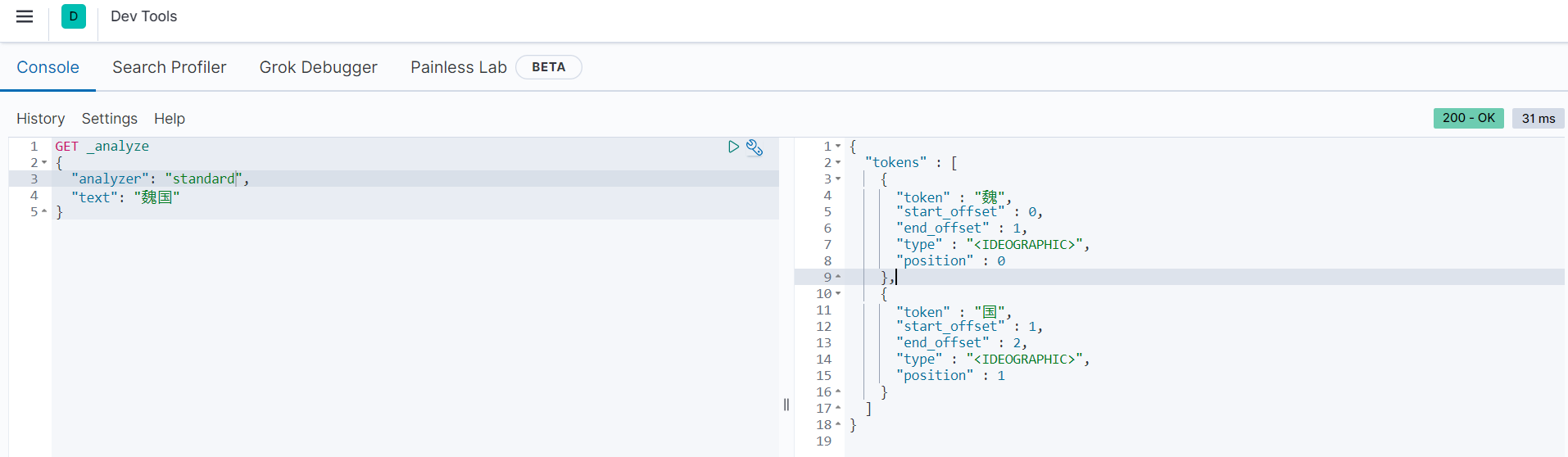
可以看到,”魏国“被分词后还是”魏国“。而我们在查询的时候,是根据standard分词器默认进行分词的,会把单个汉字作为一个词(term),如下图所示:
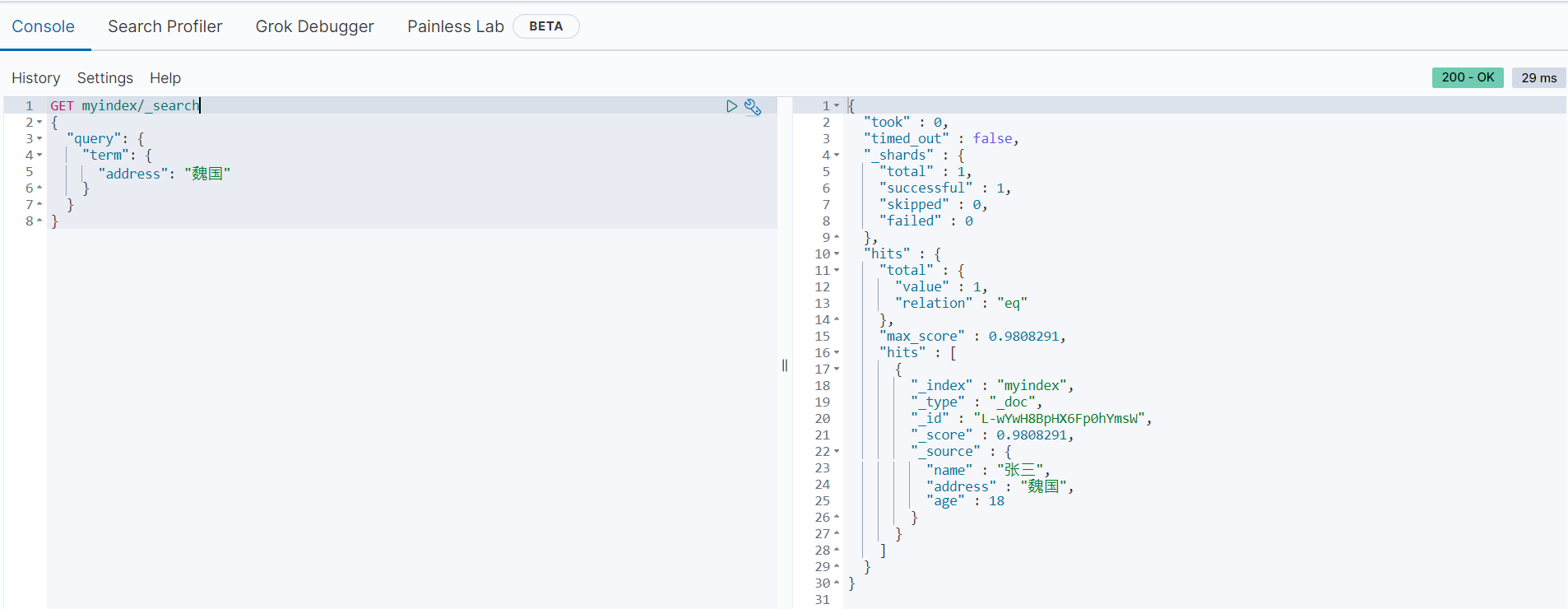
可以看到,“魏国”被分成单独的两个汉字“魏”和“国”。在查询时,就是在“魏国”、“蜀国”、“吴国”三个词中去匹配是否有等于“魏”或“国”的数据,所以就导致没有查询出任何结果。对于这种情况,可以使用term进行查询,把“魏国”当作一个单独的词不进行分词,然后进行查询。范例如下:
GET myindex/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"address": "魏国"
}
}
}返回结果如下
bool多条件查询
在使用Elasticsearch查询时,如果想要构造更复杂的查询(即搜索),可以使用bool来组合多个查询条件,语法如下:
GET 索引名称/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{"match": {"field1": "value1"}}
],
"must_not": [
{"match": {"field2": "value2"}}
]
}
}
}范例如下:
POST myindex/_bulk
{"index": {}}
{"name": "张三", "address": "中国上海", "age": 18}
{"index": {}}
{"name": "李四", "address": "中国杭州", "age": 18}
{"index": {}}
{"name": "王五", "address": "中国杭州", "age": 19}
{"index": {}}
{"name": "赵六", "address": "中国上海", "age": 20}
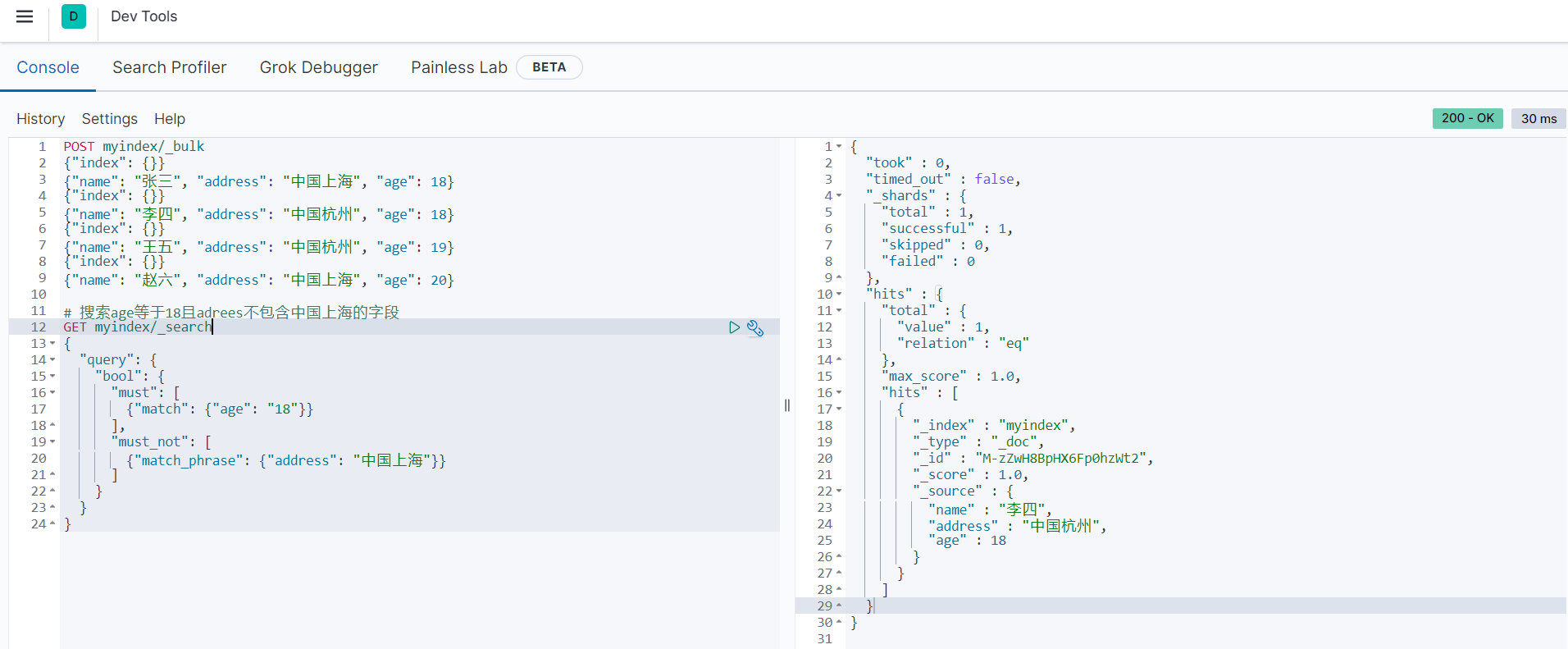
# 搜索age等于18且adrees不包含中国上海的字段
GET myindex/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{"match": {"age": "18"}}
],
"must_not": [
{"match_phrase": {"address": "中国上海"}}
]
}
}
}返回结果如下:
bool和filter组合查询
下面的范例使用bool和filter组合查询
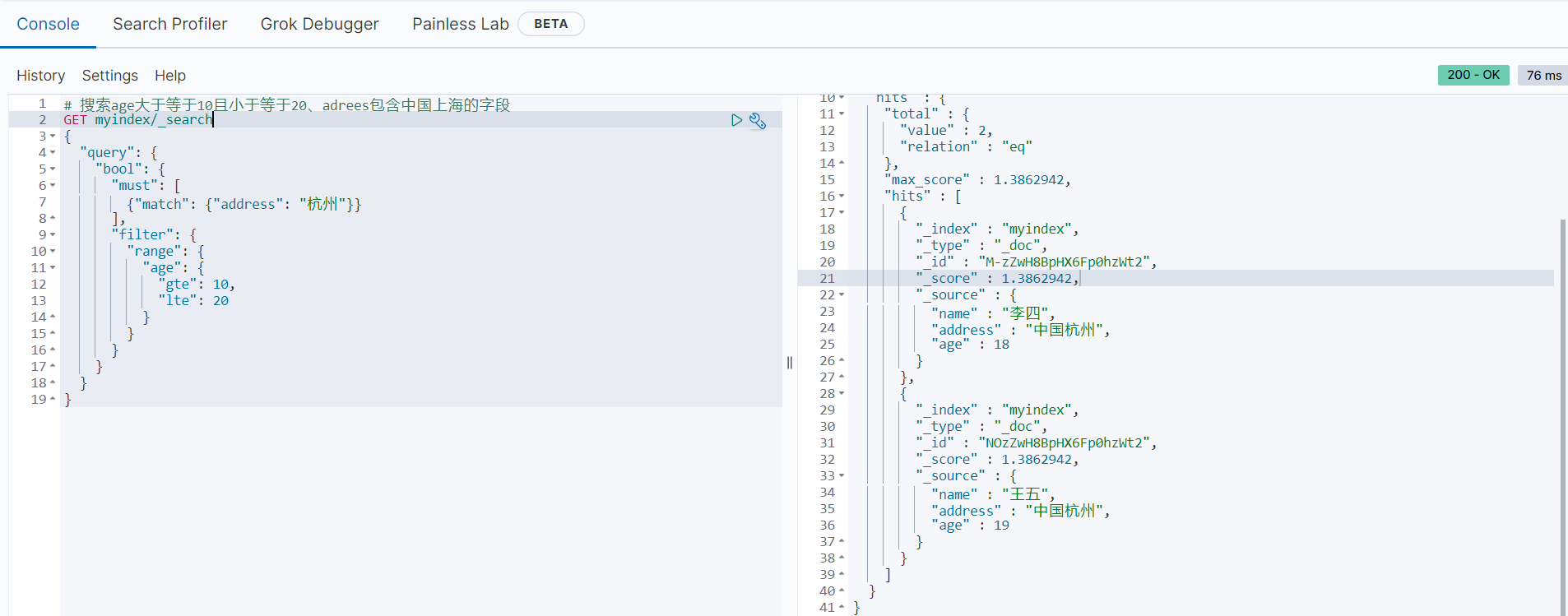
# 搜索age大于等于10且小于等于20、adrees包含中国上海的字段
GET myindex/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{"match": {"address": "杭州"}}
],
"filter": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 10,
"lte": 20
}
}
}
}
}
}返回结果如下:
简单的聚合查询
我们知道在SQL语句中有group by,而在Elasticsearch中把它叫Aggregation,即聚合运算。下面通过范例来理解和学习聚合查询。
范例数据如下:
POST myindex/_bulk
{"index": {}}
{"name": "张三", "address": "上海", "age": 18, "score": 60}
{"index": {}}
{"name": "李四", "address": "杭州", "age": 18, "score": 70}
{"index": {}}
{"name": "王五", "address": "杭州", "age": 20, "score": 80}
{"index": {}}
{"name": "赵六", "address": "上海", "age": 21, "score": 90}分组统计各组的总条数
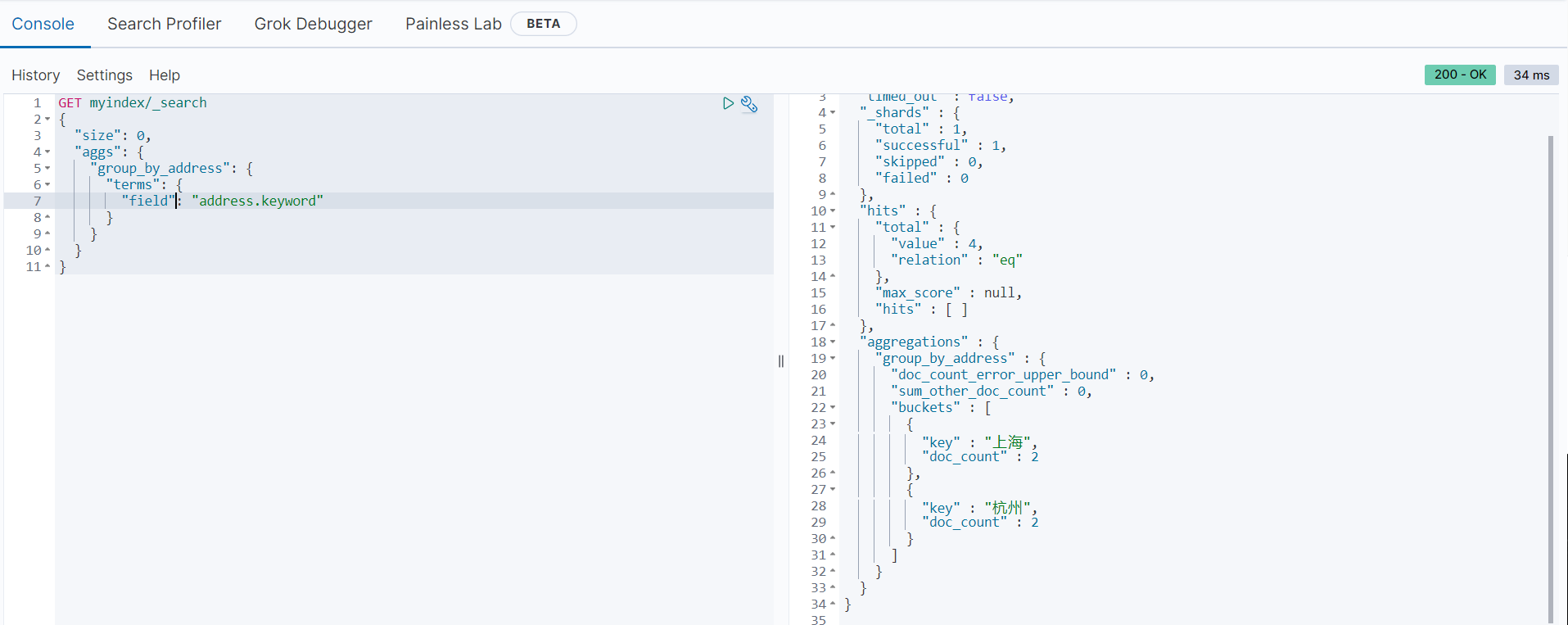
以下范例是按地址进行分组,统计每个地址的考试人数
GET myindex/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_address": {
"terms": {
"field": "address.keyword"
}
}
}
}返回结果如下:
分组统计每组平均值
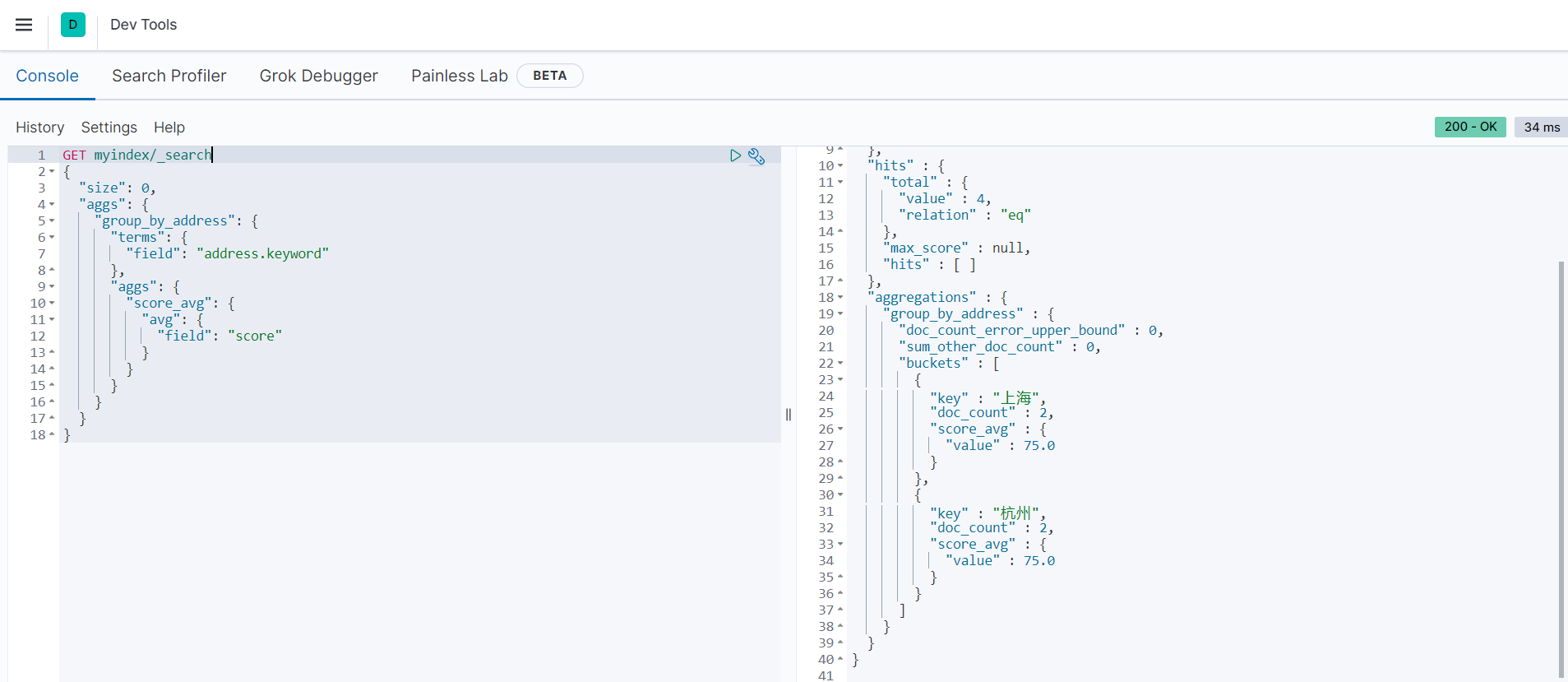
以下范例是按地址进行分组,统计每个地址平均分:
GET myindex/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_address": {
"terms": {
"field": "address.keyword"
},
"aggs": {
"score_avg": {
"avg": {
"field": "score"
}
}
}
}
}
}返回结果如下:
分组统计每组的最大值
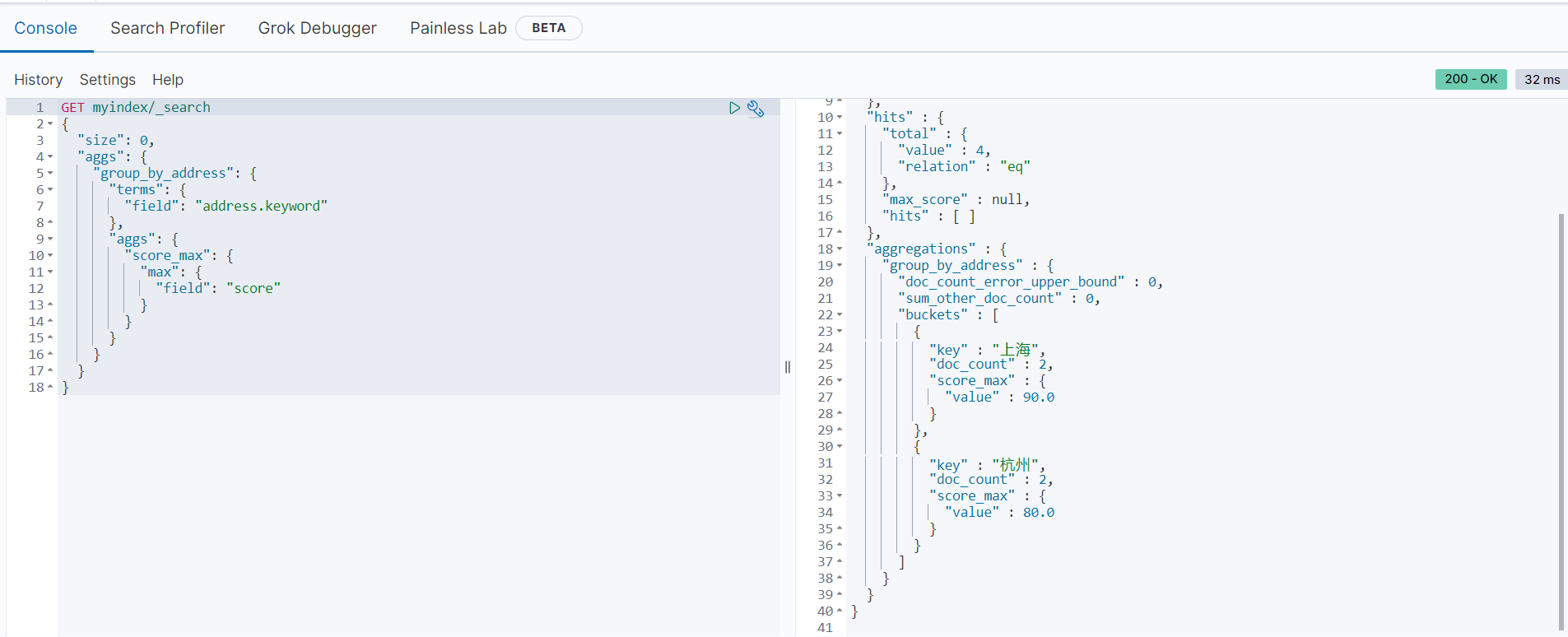
以下范例是按地址进行分组,统计每个地址的最高分数:
GET myindex/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_address": {
"terms": {
"field": "address.keyword"
},
"aggs": {
"score_max": {
"max": {
"field": "score"
}
}
}
}
}
}返回结果如下:
分组统计每组的最小值
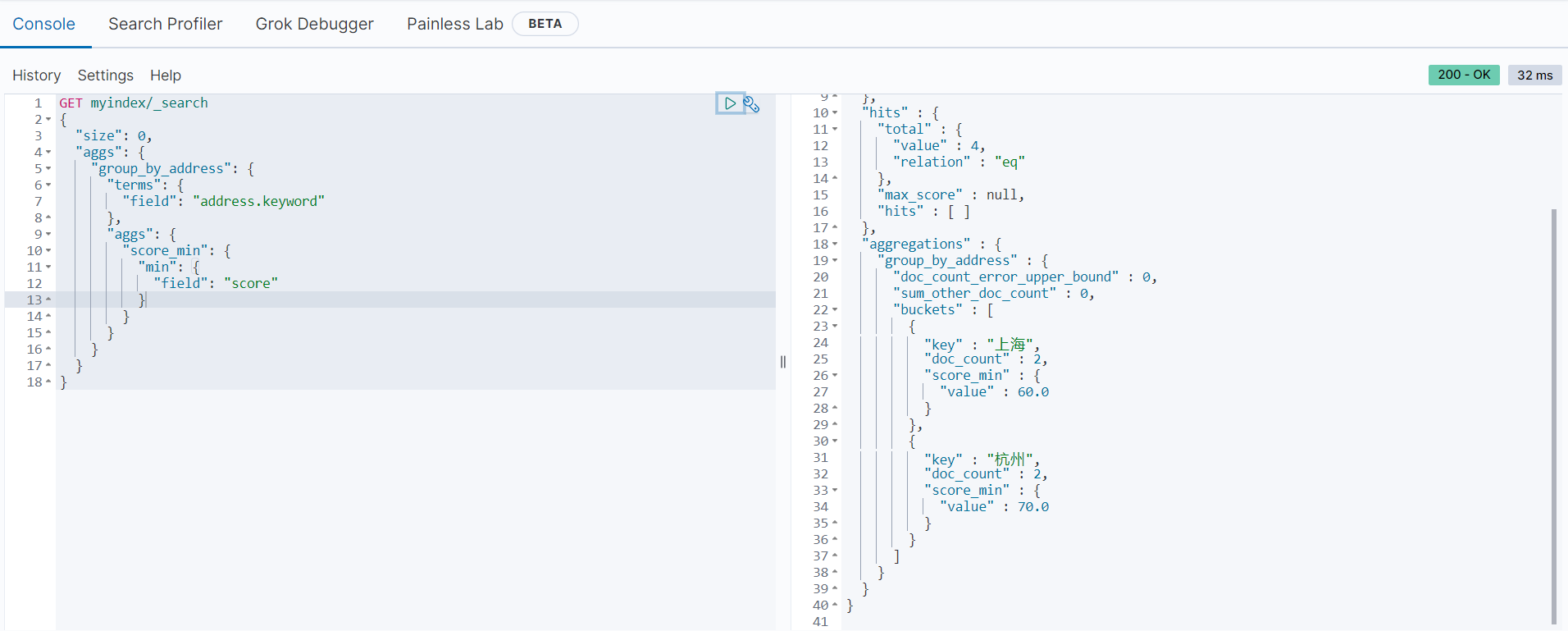
以下范例是按地址进行分组,统计每个地址的最低分数:
GET myindex/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_address": {
"terms": {
"field": "address.keyword"
},
"aggs": {
"score_min": {
"min": {
"field": "score"
}
}
}
}
}
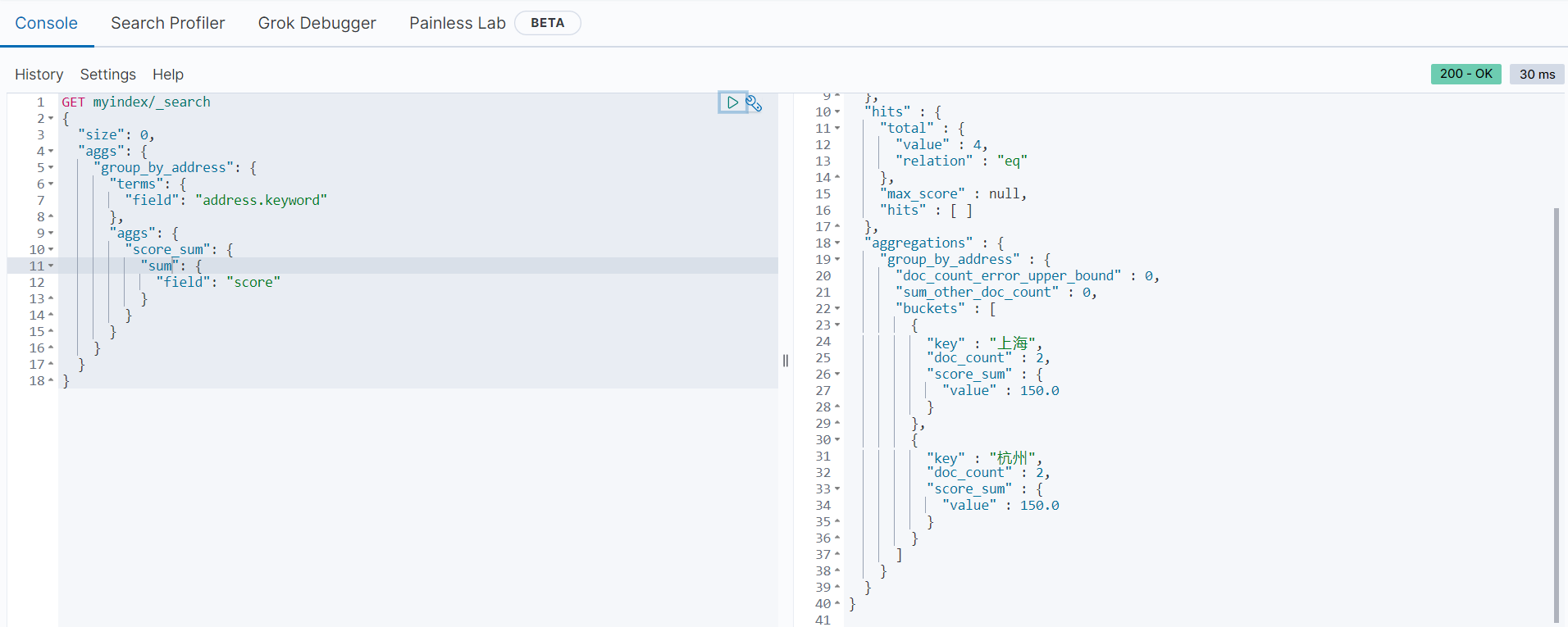
}分组统计每组的总和
以下范例是按地址进行分组,统计每个地址的总分数:
GET myindex/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_address": {
"terms": {
"field": "address.keyword"
},
"aggs": {
"score_sum": {
"sum": {
"field": "score"
}
}
}
}
}
}返回结果如下:
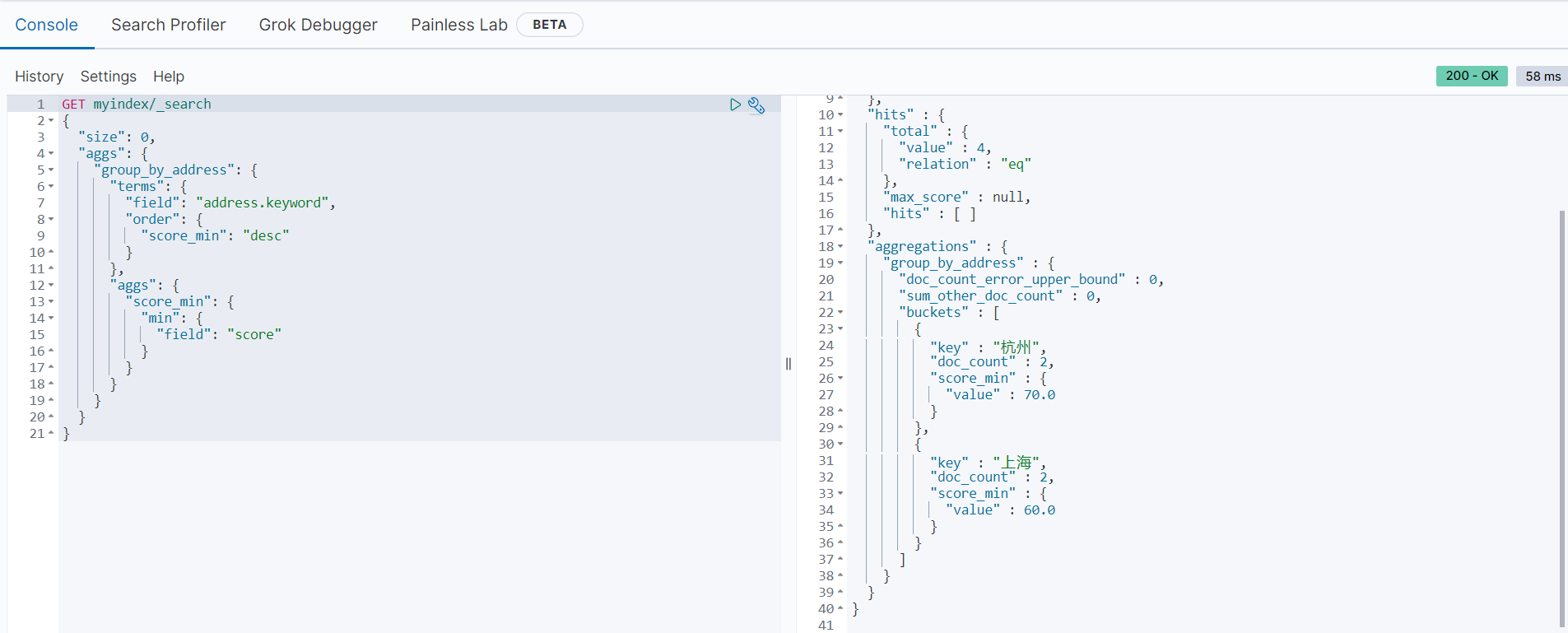
分组统计每组的最小值并按统计结果排序
以下范例是按地址进行分组,统计每个地址的最低分数并根据统计结果倒序返回结果:
GET myindex/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_address": {
"terms": {
"field": "address.keyword",
"order": {
"score_min": "desc"
}
},
"aggs": {
"score_min": {
"min": {
"field": "score"
}
}
}
}
}
}返回结果如下: